 Engine Management Technology Engine Management Technology
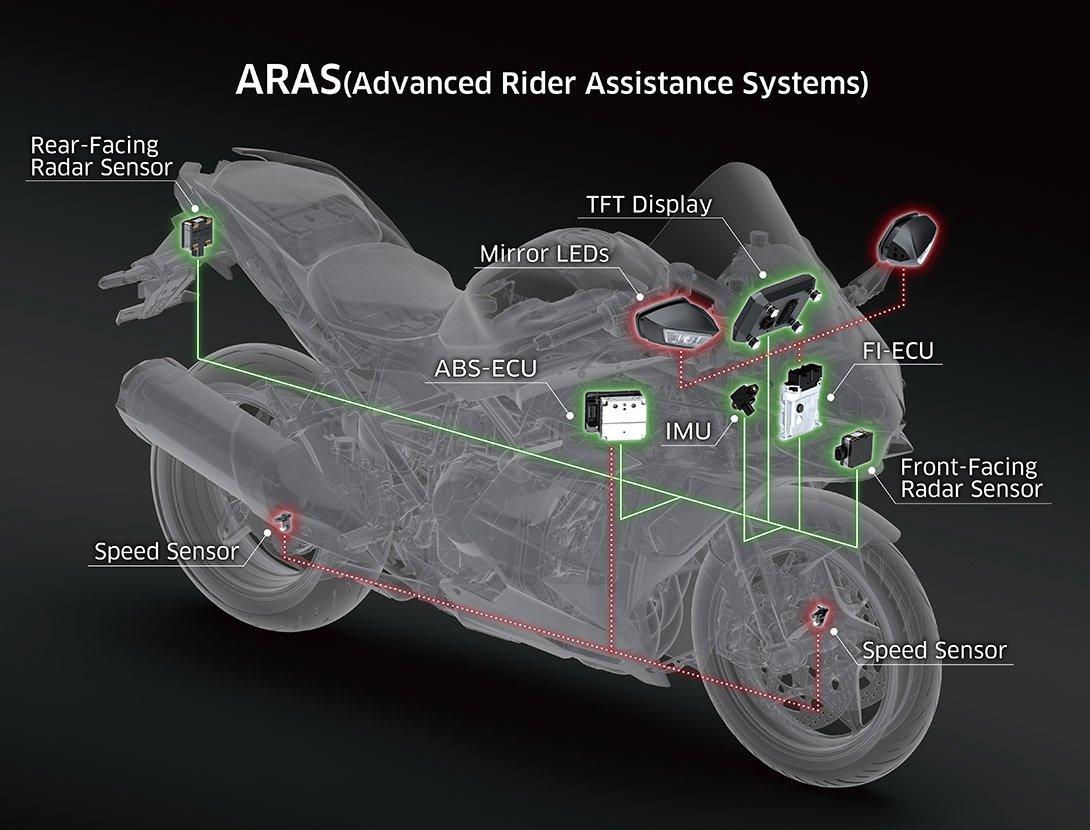
ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control)
ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control):
A more advanced version of Electronic Cruise Control, ACC maintains the speed set by the rider, but adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a suitable following distance from the vehicle in front.
A front-facing radar sensor uses millimetre-wave radar to scan ahead in the rider’s lane. The system takes into account the proximity of the vehicle ahead, degree of road slope, front/rear wheel speed, and the rider-selected distance setting (Near, Medium, or Far).
When the distance to the vehicle in front is deemed insufficient, the system directs speed to be reduced. When the necessary decrease in speed is not great, this can be accomplished with engine braking; when stronger deceleration is required, the system also activates the brakes. Once more space becomes available, the system directs speed to be increased and the throttle is increased to return to the set speed. |
ASSIST & SLIPPER CLUTCH

Based on feedback from racing activities, the Assist & Slipper Clutch uses two types of cams (an assist cam and a slipper cam) to either drive the clutch hub and operating plate together or apart.
Under normal operation, the assist cam functions as a self-servo mechanism, pulling the clutch hub and operating plate together to compress the clutch plates. This allows the total clutch spring load to be reduced, resulting in a lighter clutch lever feel when operating the clutch.
When excessive engine braking occurs – as a result of quick downshifts (or an accidental downshift) – the slipper cam comes into play, forcing the clutch hub and operating plate apart. This relieves pressure on the clutch plates to reduce back-torque and helps prevent the rear tire from hopping and skidding. This race-style function is particularly useful when sport or track riding. |
 ECONOMICAL RIDING INDICATOR ECONOMICAL RIDING INDICATOR
Using high-precision electronic control for engine management, Kawasaki models can achieve a high level of fuel efficiency. However, fuel consumption is greatly affected by throttle use, gear selection, and other elements under the rider's control. The Economical Riding Indicator is a function that indicates when current riding conditions are consuming a low amount of fuel. The system continuously monitors fuel consumption, regardless of vehicle speed, engine speed, throttle position and other riding conditions. When fuel consumption is low for a given speed (i.e. fuel efficiency is high), an "ECO" mark appears on the instrument panel's LCD screen. By riding so that the "ECO" mark remains on, fuel consumption can be reduced.
While effective vehicle speed and engine speed may vary by model, paying attention to conditions that cause the "ECO" mark to appear can help riders improve their fuel efficiency – a handy way to increase cruising range. Further, keeping fuel consumption low also helps minimize negative impact on the environment. |
ELECTRONIC THROTTLE VALVES
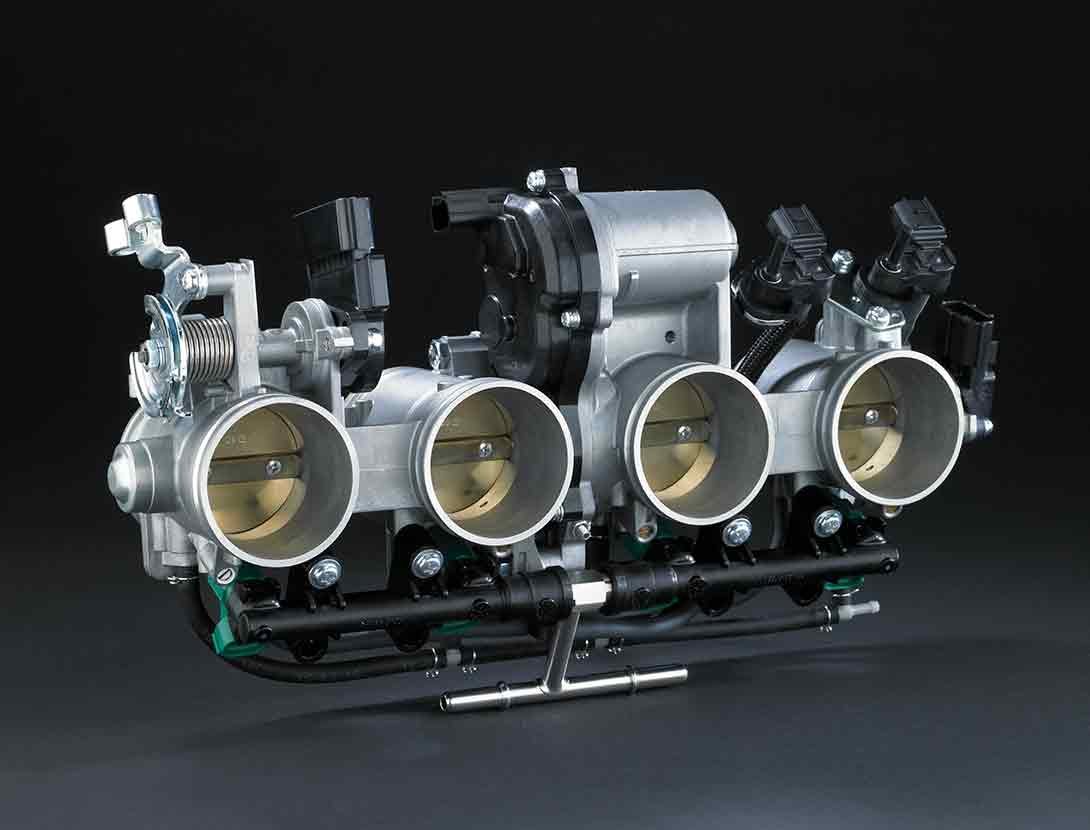

Kawasaki’s fully electronic throttle actuation system enables the ECU to control the volume of both the fuel (via fuel injectors) and the air (via throttle valves) delivered to the engine. Ideal fuel injection and throttle valve position results in smooth, natural engine response and the ideal engine output. The system also makes a significant contribution to reduced emissions.
Electronic throttle valves also enable more precise control of electronic engine management systems like S-KTRC and KTRC, and allow the implementation of electronic systems like KLCM, Kawasaki Engine Brake Control, and Electronic Cruise Control. |
KAWASAKI ENGINE BRAKE CONTROL The Kawasaki Engine Brake Control system allows riders to select the amount of engine braking they prefer. When the system is activated, the engine braking effect is reduced, providing less interference when riding on the track. |
KCMF (KAWASAKI CORNERING MANAGEMENT FUNCTION)
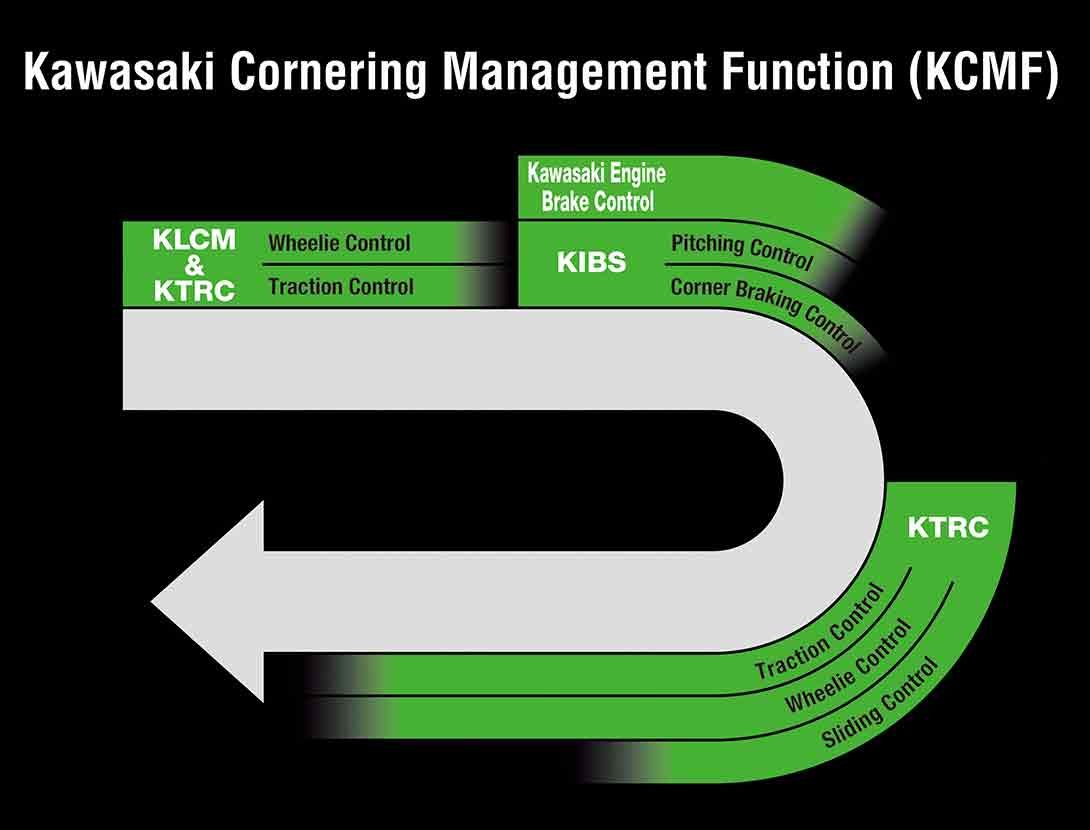 Using the latest evolution of Kawasaki’s advanced modeling software and feedback from a compact IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) that gives an even clearer real-time picture of chassis orientation, KCMF monitors engine and chassis parameters throughout the corner – from entry, through the apex, to corner exit – modulating brake force and engine power to facilitate smooth transition from acceleration to braking and back again, and to assist riders in tracing their intended line through the corner. The systems that KCMF oversees vary by model, but may include:
• S-KTRC/KTRC (including traction management and wheel lift management)
• KLCM (including traction management and wheel lift management)
- Designed to optimize acceleration from a stop
• KIBS (including pitching management and corner braking management)
• Kawasaki Engine Brake Control |
KLCM (KAWASAKI LAUNCH CONTROL MODE)
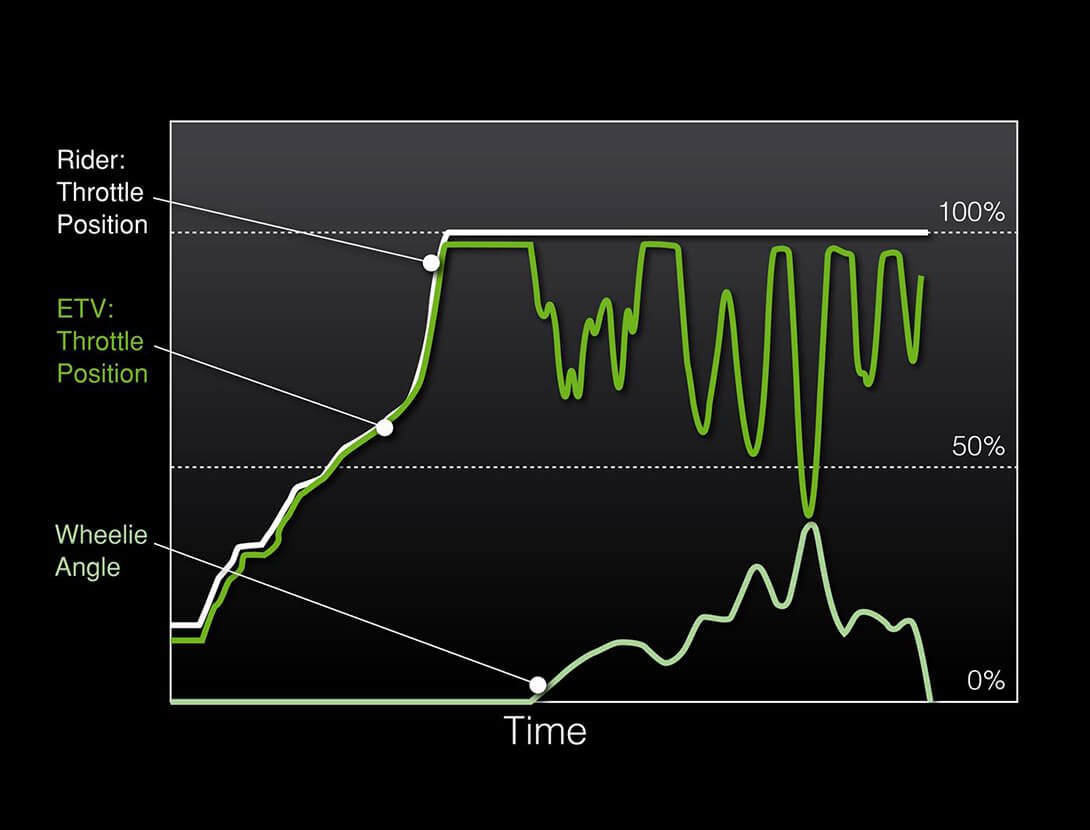
Designed to assist riders by optimizing acceleration from a stop, KLCM electronically manages engine output to minimize wheel spin when moving off. With the clutch lever pulled in and the system activated, engine speed is limited to a determined speed while the rider holds the throttle open. Once the rider releases the clutch lever to engage the clutch, engine speed is allowed to increase, but power is regulated to minimize wheel spin and help keep the front wheel on the ground. The system disengages automatically once a predetermined speed has been reached, or when the rider shifts into third gear. Depending on the model, riders can choose from multiple modes, each offering a progressively greater level of intrusion.
|
KQS (KAWASAKI QUICK SHIFTER)
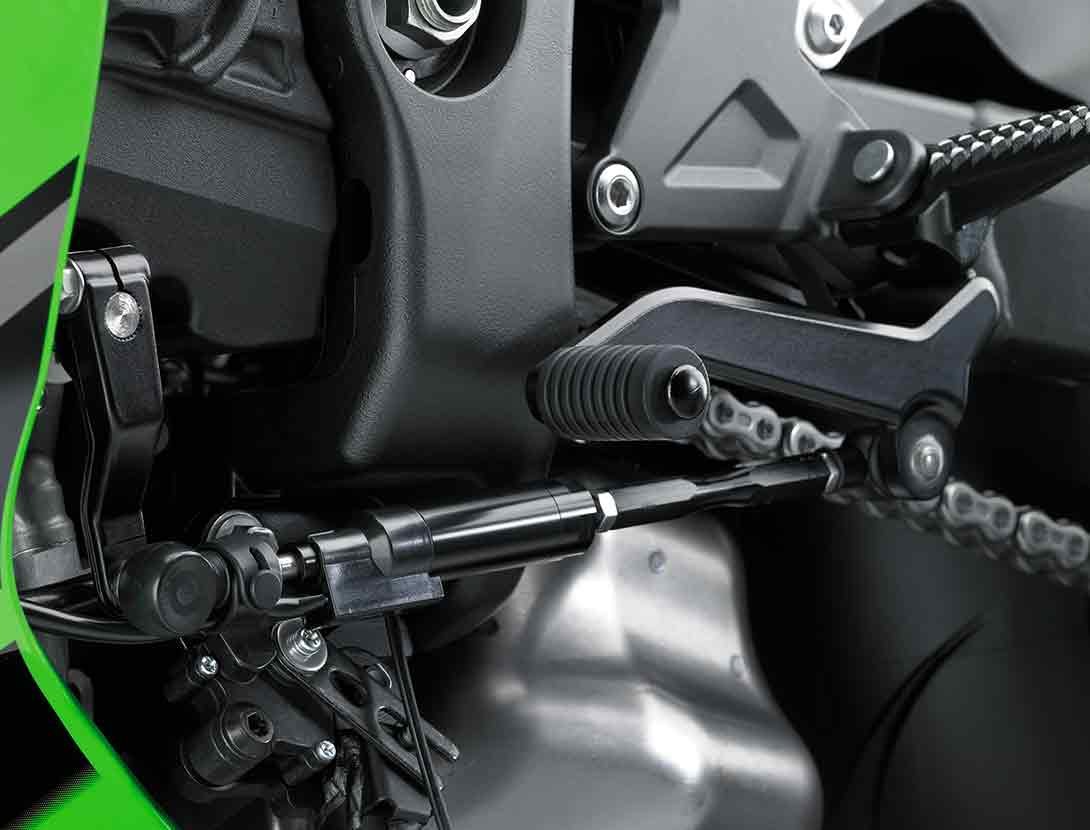 Designed to help riders maximize their acceleration on the track by enabling clutchless upshifts with the throttle fully open, KQS detects that the shift lever has been actuated and sends a signal to the ECU to cut ignition so that the next gear can be engaged without having to use the clutch. On models that offer clutchless downshifts, during deceleration the system automatically controls engine speed so that the next lower gear can be selected without operating the clutch. |
 KTRC (KAWASAKI TRACTION CONTROL) KTRC (KAWASAKI TRACTION CONTROL)
KTRC, Kawasaki's advanced traction control system provides both enhanced sport riding performance and the peace of mind to negotiate slippery surfaces with confidence. Multiple rider-selectable modes (the number of modes varies by model) offer progressively greater levels of intrusion to suit the riding situation and rider preference.
Less intrusive modes maintain optimum traction during cornering. Designed with sport riding in mind, they facilitate acceleration out of corners by maximizing forward drive from the rear wheel. And because Kawasaki’s sophisticated software bases its dynamic analysis on the chassis’ orientation relative to the track surface (rather than relative to a horizontal plane), it is able to take into account corner camber, gradient, etc., and adapt accordingly.
In the more intrusive modes (and for some models, in any mode), when excessive wheel spin is detected, engine output is reduced to allow grip to be regained, effectively enabling riders to negotiate both short, slippery patches (train tracks or manhole covers) and extended stretches of bad roads (wet pavement, cobblestone, gravel) with confidence.
Models equipped with IMU incorporate chassis-orientation feedback to offer even more precise management. |
POWER MODES
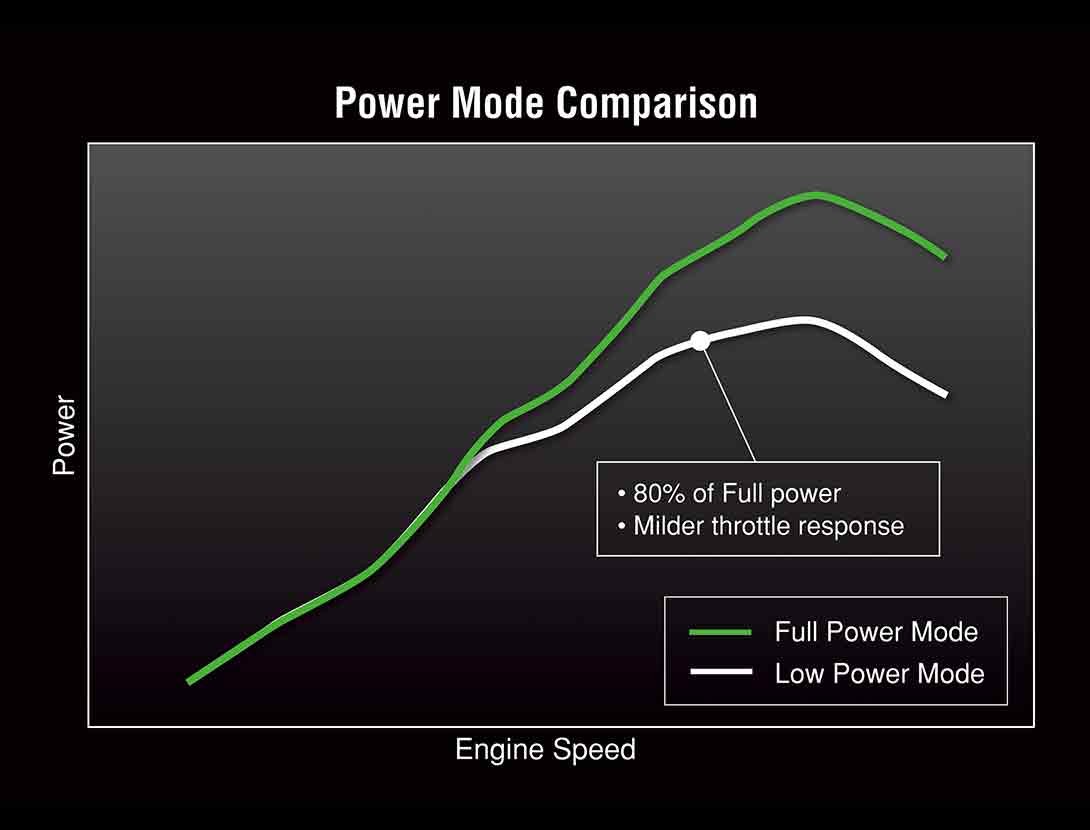 Models equipped with multiple Power Modes offer riders an easily selectable choice of engine power delivery to suit riding conditions or preference. In addition to Full Power mode, one (Low) or two (Middle, Low) alternate mode(s) in which maximum power is limited and throttle response is milder are provided. |
SMARTPHONE CONNECTIVITY
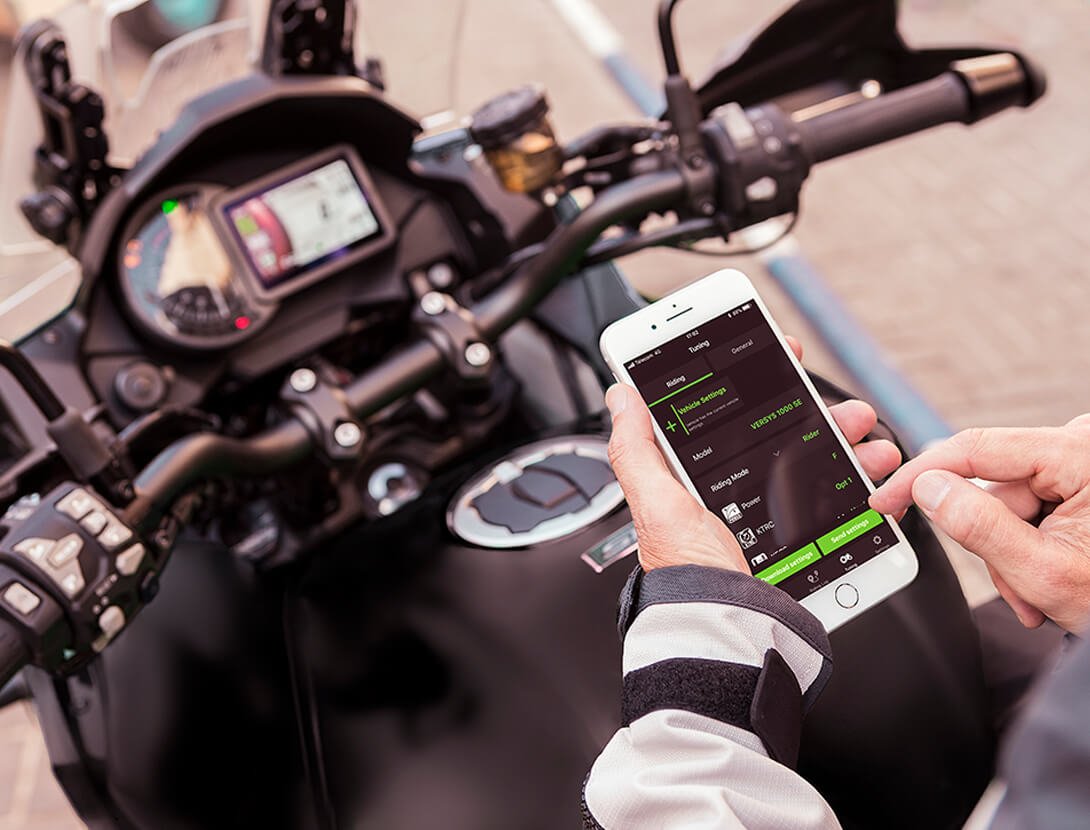 Clever technology enables riders to connect to their motorcycle wirelessly. Using the smartphone application “RIDEOLOGY THE APP,” a number of instrument functions can be accessed, contributing to an enhanced motorcycling experience. Vehicle information (such as the odometer, fuel gauge, maintenance schedule, etc) can be viewed on the smartphone. Riding logs (varies by model, but may include GPS route, gear position, rpm, and other information) can be viewed on the smartphone. When connected, telephone (call, mail) notices are displayed on the instrument panel. Riders can also make changes to their motorcycle’s instrument display settings (preferred units, clock and date setting, etc) via the smartphone. And on certain models, it is even possible to check and adjust vehicle settings (such as Rider Mode, electronic rider support features, and payload settings) using the smartphone. |
SUPERCHARGED ENGINE
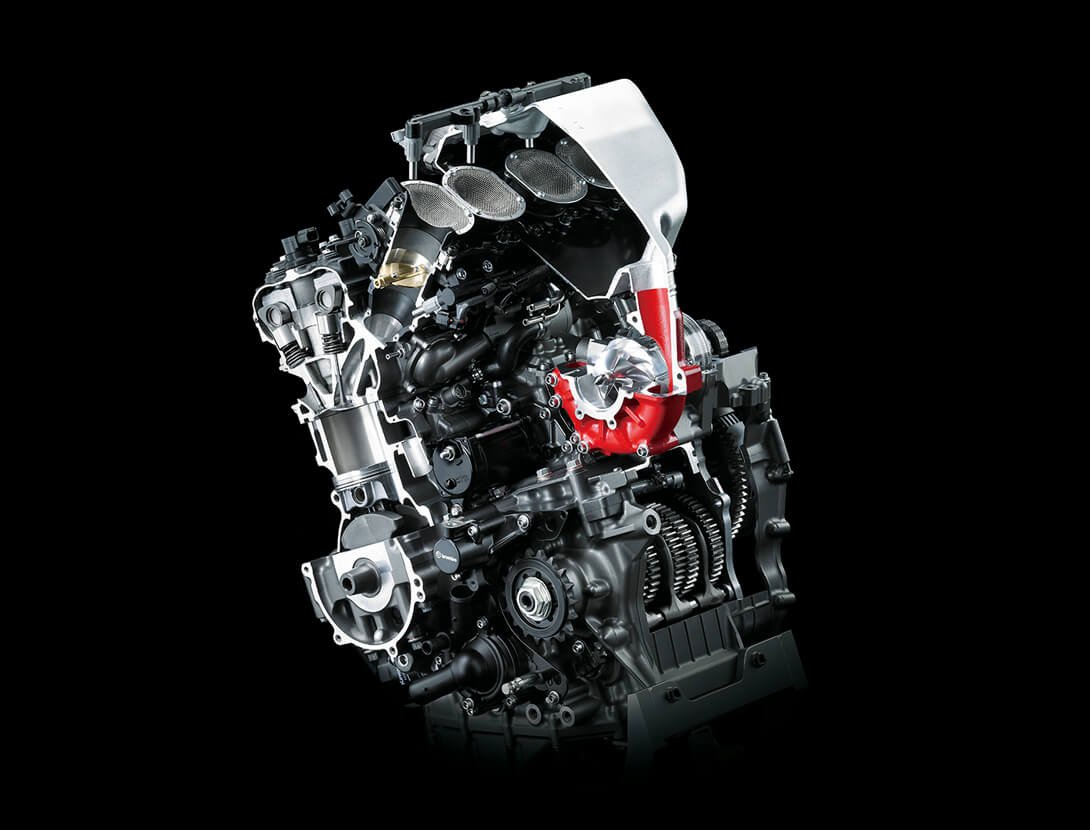

Drawing on the know-how and technology possessed by the Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (KHI), Kawasaki’s supercharged engine delivers high engine output while maintaining a compact design. The key to achieving this incredible performance lies in the engine’s supercharger – a motorcycle-specific unit designed completely in-house with technology from the Kawasaki Gas Turbine & Machinery Company, Aerospace Company and Corporate Technology Division.
One of the greatest benefits of designing the supercharger in-house and tailoring its design to match the engine’s characteristics was that engineers were able to achieve high-efficiency operation over a wide range of conditions – something that would not have been possible by simply dropping in or trying to adapt an aftermarket automotive supercharger.
The importance of high efficiency in a supercharger is that, as the air is compressed, power-robbing heat gain is minimal. And while many superchargers are able to offer high-efficiency operation in a very limited range of conditions, the Kawasaki supercharger offers high efficiency over a wide range of pressure ratios and flow rates – meaning over a wide range of engine speeds and vehicle speeds. This wide range of efficient operation (similar to having a wide power band) easily translates to strong acceleration. The supercharger’s high efficiency and minimal heat gain also meant that an intercooler was unnecessary, greatly saving weight and space, and enabling the engine’s compact design. |
Chassis Management Technology
ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
Kawasaki ABS systems use front and rear wheel sensors to constantly monitor wheel speed. Should information from either of the sensors indicate that wheel lock has occurred, the ABS ECU directs the pump in the ABS unit to modulate brake fluid pressure (releasing and reapplying pressure so that traction can be regained) until normal operation resumes. ABS offers rider reassurance that contributes to greater riding enjoyment. |
AHB (Auto High Beam)

Using a camera sensor to assess the brightness of the lights of vehicles ahead, of streetlights, etc, AHB automatically turns the bike’s high beams on or off as necessary.
For the system to function, the dimmer/passing switch must be set to high beam, the bike must be travelling above 20 km/h, and it must be dark. When the system has been engaged, the icon displayed on the instrument screen will show green. |
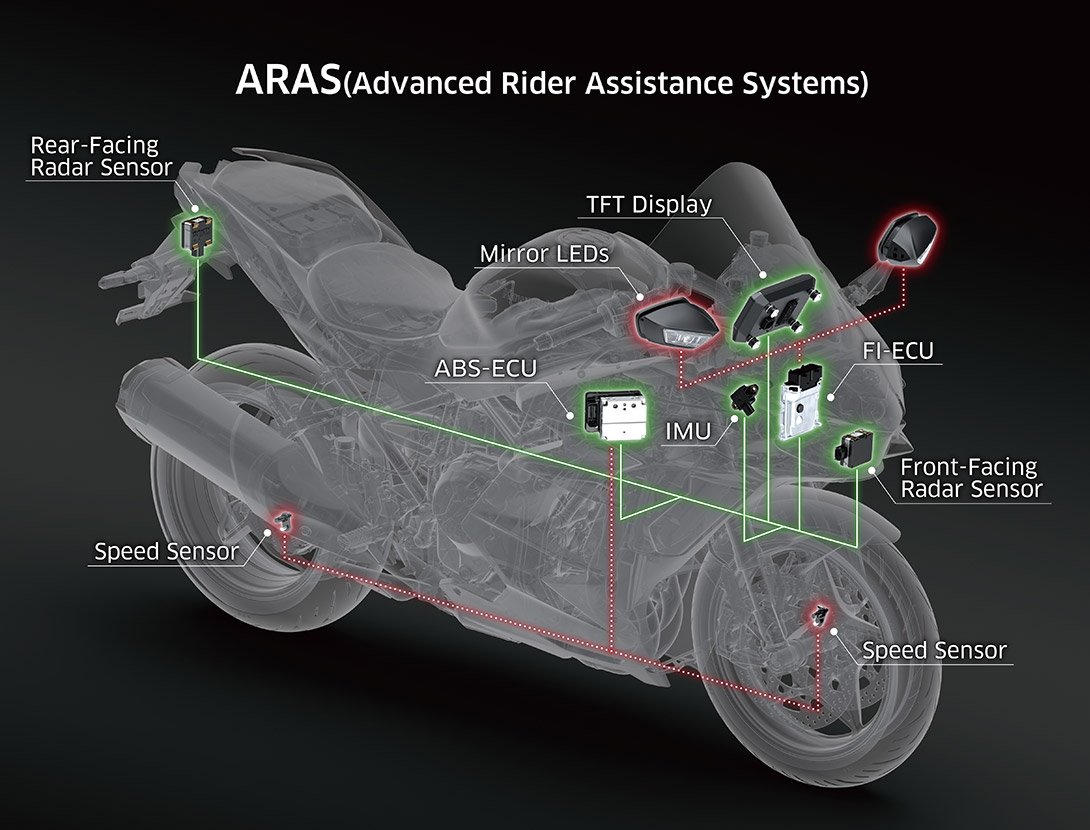
BSD (Blind-Spot Detection)
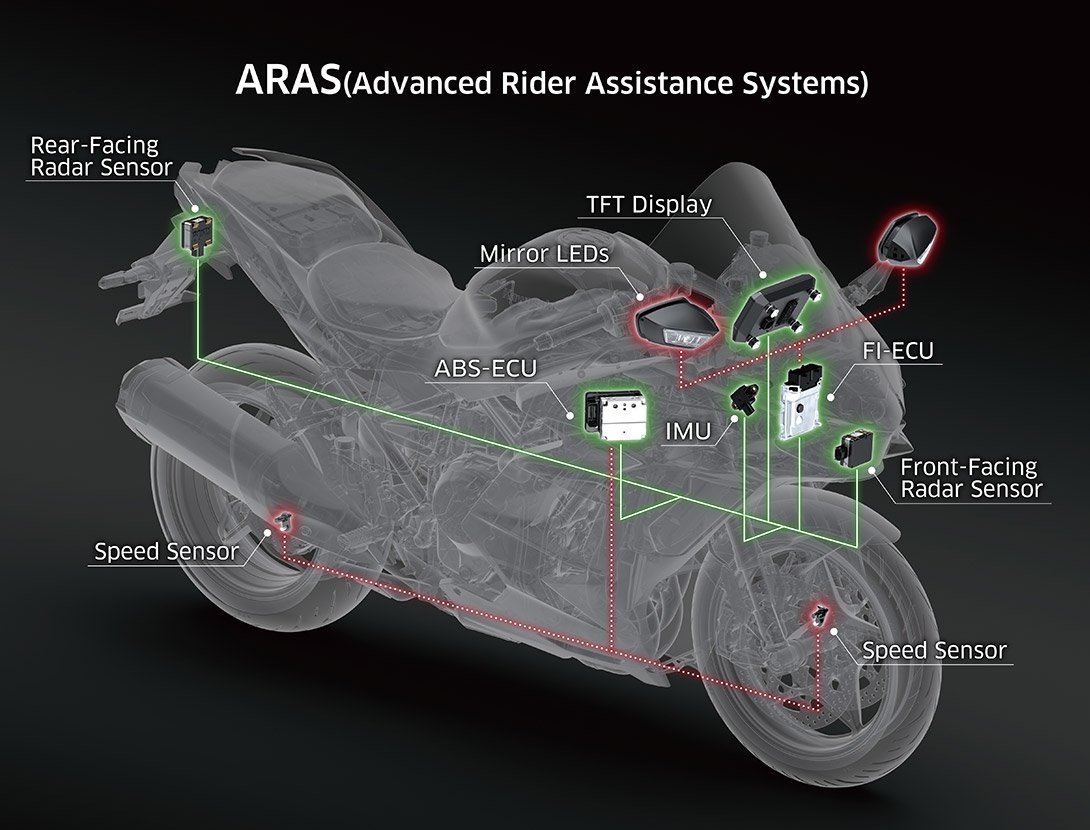
BSD (Blind-Spot Detection):
Using a rear-facing radar sensor, BSD monitors the bike’s surroundings and alerts the rider to presence of a vehicle approaching in the rider’s blind spot.
The rear-facing radar sensor scans behind in the lanes to the left and right of the rider. When an approaching vehicle is detected, an LED built into the rearview mirror will light up. (Note: BSD will not alert the rider to vehicles directly behind the bike, or vehicles that are moving away from the bike.)
Should the rider indicate the intent to change lanes by switching on their turn signal while a vehicle is detected in a blind spot, the mirror LED will flash. |
Cornering Lights

A set of three LED lights built into each side of the fairing help illuminate the road when cornering at night. Each of the three lights has a fixed direction and is activated based on lean angle. As the bike leans over, the lights come on in order, creating a wider illuminated path in the direction the bike is heading. |
 FCW (Forward Collision Warning) FCW (Forward Collision Warning)
FCW (Forward Collision Warning):
When the system determines that continuing at the current speed may result in a collision with the vehicle in front, it warns the rider.
A front-facing radar sensor monitors the distance and speed of the vehicle in front. When a vehicle is in close proximity and there is danger of a collision should the current speed be maintained, the system alerts the rider using a bright flashing red LED light above the instrument panel. A warning is also shown on the TFT display.
Riders can set the alert timing according to preference: Early, Medium, Late. |
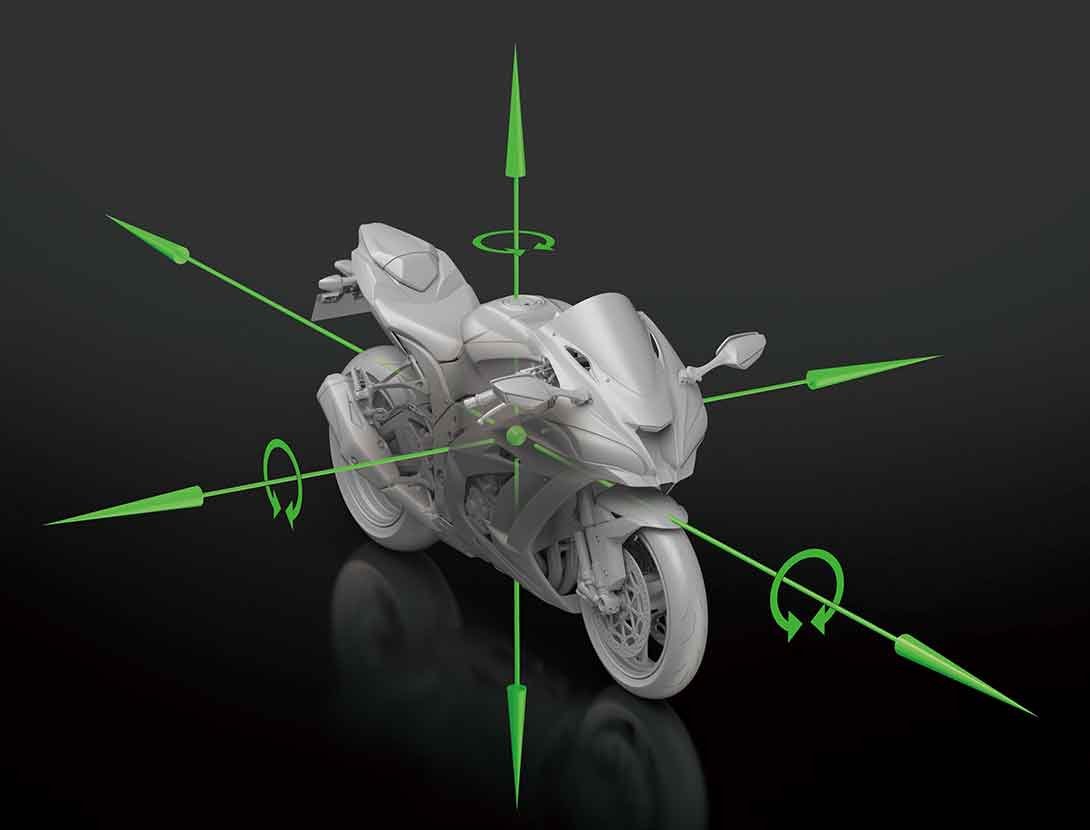 IMU-ENHANCED CHASSIS ORIENTATION AWARENESS IMU-ENHANCED CHASSIS ORIENTATION AWARENESS
The strength of Kawasaki’s cutting-edge electronics has always been the highly sophisticated programming that, using minimal hardware, gives the ECU an accurate real-time picture of what the chassis is doing. Kawasaki’s proprietary dynamic modeling program makes skillful use of the magic formula tire model as it examines changes in multiple parameters, enabling it to take into account changing road and tire conditions.
The addition of an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) enables inertia along 6 DOF (degrees of freedom) to be monitored. Acceleration along longitudinal, transverse and vertical axes, plus roll rate and pitch rate are measured. The yaw rate is calculated by the ECU using Kawasaki original software. This additional feedback contributes to an even clearer real-time picture of chassis orientation, enabling even more precise management for control at the limit.
With the addition of the IMU and the latest evolution of Kawasaki’s advanced modeling software, Kawasaki’s electronic engine and chassis management technology takes the step to the next level – changing from setting-type and reaction-type systems to feedback-type systems – to deliver even greater levels of riding excitement. |
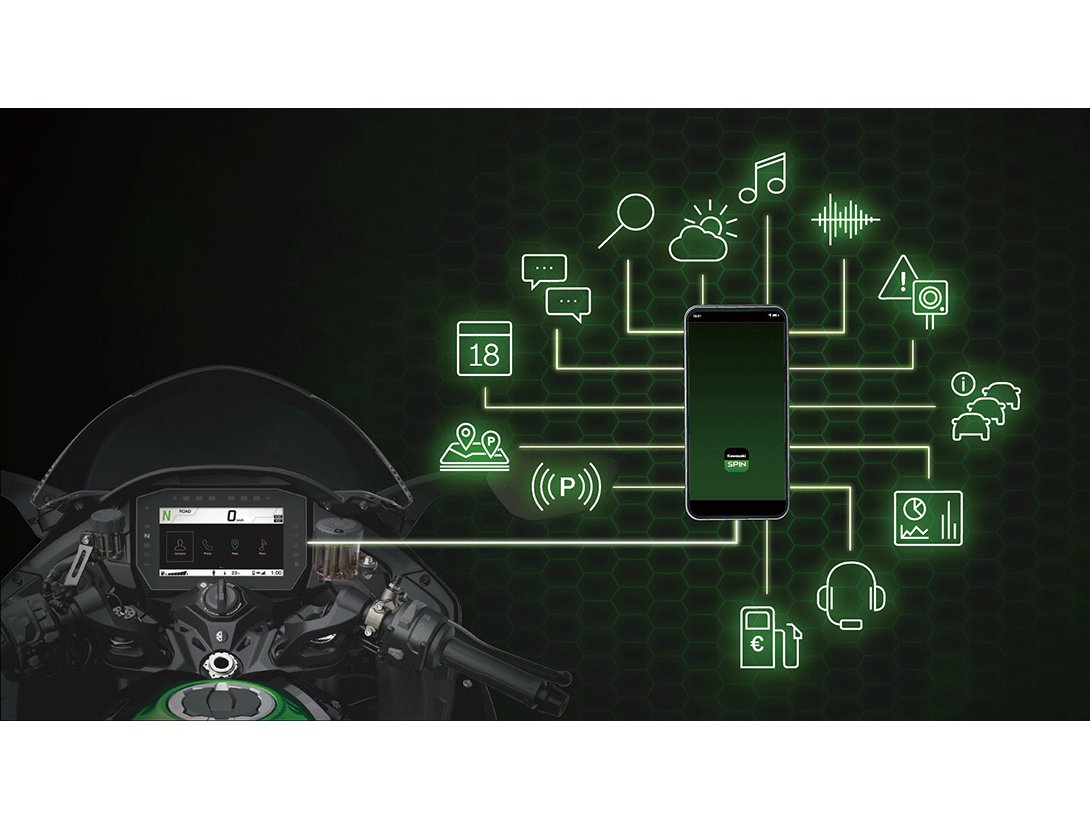 Kawasaki SPIN Kawasaki SPIN
Kawasaki SPIN:
Kawasaki’s new smartphone-based infotainment app enables various third-party applications to be downloaded and mirrored on the cockpit’s TFT display. Basic functions available in the app include telephone, map display, music, calendar, and contacts. Additionally, riders can opt to download third-party apps to add to their Kawasaki SPIN library to be able to interact with them on the TFT display. |
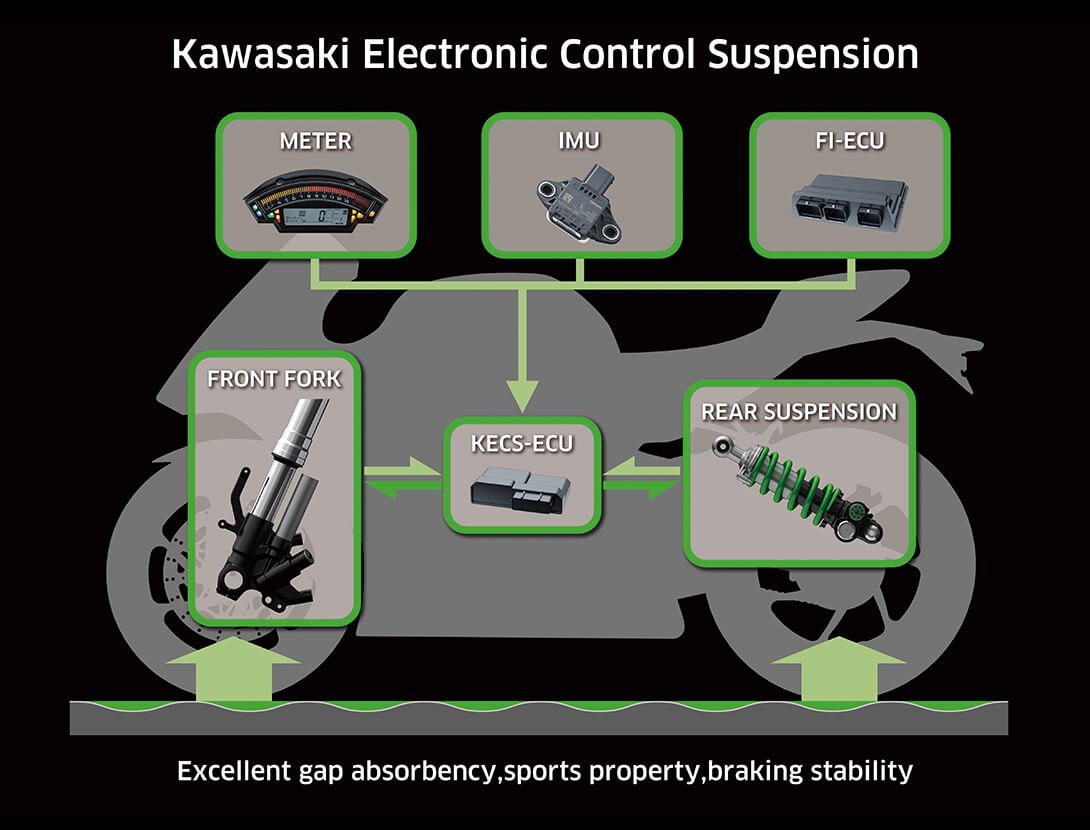 KECS (KAWASAKI ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION) KECS (KAWASAKI ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION)
KECS adapts to road and riding conditions in real time, providing the ideal amount of damping called for by electronically adjusting damping to suit vehicle speed and suspension stroke speed. Deceleration is also taken into account, which allows the system to help manage pitching that may occur during braking.
Control via solenoid valve with direct actuation enables an extremely quick reaction time, making KECS ideal for sport riding applications, where natural feeling is crucial to feeling at one with the bike. Built-in stroke sensors on both the fork and rear shock provide real-time stroke speed and compression information. Input from the sensor coils to the KECS ECU is complemented by information provided by the IMU (acceleration/deceleration) and the FI ECU (vehicle speed). The KECS ECU then directs current to the solenoids to adjust damping as required by the situation.
Selectable modes allow riders to choose softer or firmer base settings. |
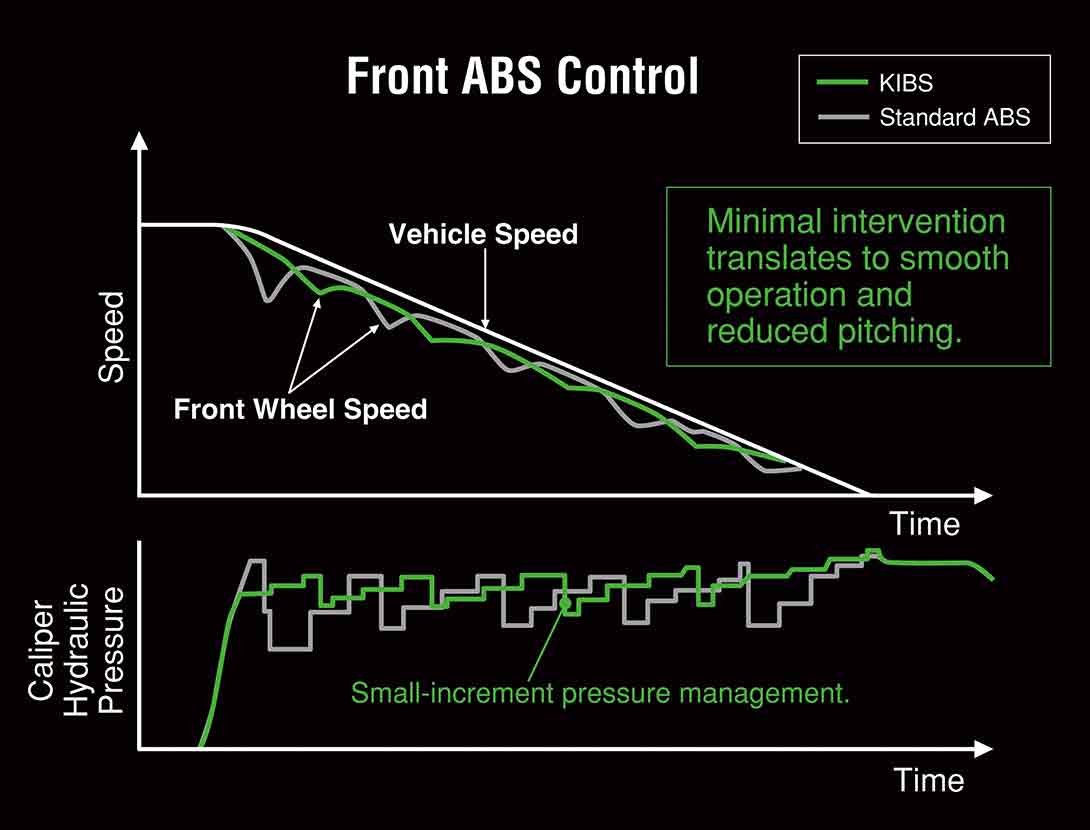 KIBS (KAWASAKI INTELLIGENT ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) KIBS (KAWASAKI INTELLIGENT ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
Kawasaki developed KIBS to take into account the particular handling characteristics of supersport motorcycles, ensuring highly efficient braking with minimal intrusion during sport riding. It is the first mass-production brake system to link the ABS ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and engine ECU.
In addition to front and rear wheel speed, KIBS monitors front brake caliper hydraulic pressure, throttle position, engine speed, clutch actuation and gear position. This diverse information is analyzed to determine the ideal front brake hydraulic pressure. Through precise control, hydraulic pressure is modulated in much smaller increments than with standard ABS systems. The system limits rear wheel lift under heavy braking and takes downshifting into account while braking, allowing the rider to manage the rear brake. And because of the finer control, kickback to the brake lever is minimal, resulting in a very natural feeling. |
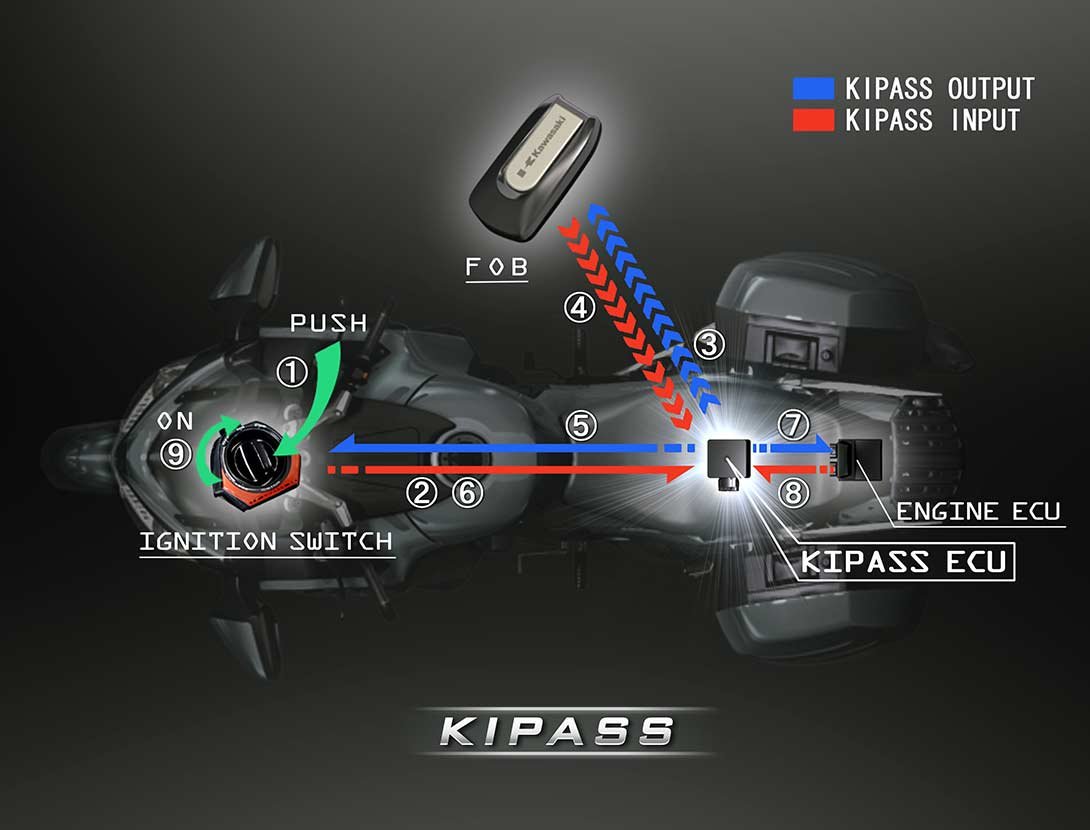 KIPASS (KAWASAKI'S INTELLIGENT PROXIMITY ACTIVATION START SYSTEM) KIPASS (KAWASAKI'S INTELLIGENT PROXIMITY ACTIVATION START SYSTEM)
With the compact key fob (portable immobilizer) in a pocket, KIPASS allows riders to remotely release the bike's steering lock and main switch simply by approaching the bike.
When the key fob is close to the bike, the signal it sends out is picked up and recognized by the KIPASS unit in the bike. Like immobilizer keys, each key fob has a unique signal, making this system also useful as a theft deterrent. The key fob can be recognized when in a jacket pocket, so there is no need for the rider to remove the key to operate the bike's main switch.
*This system uses the encryption algorithm "MISTY" developed by MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION. |
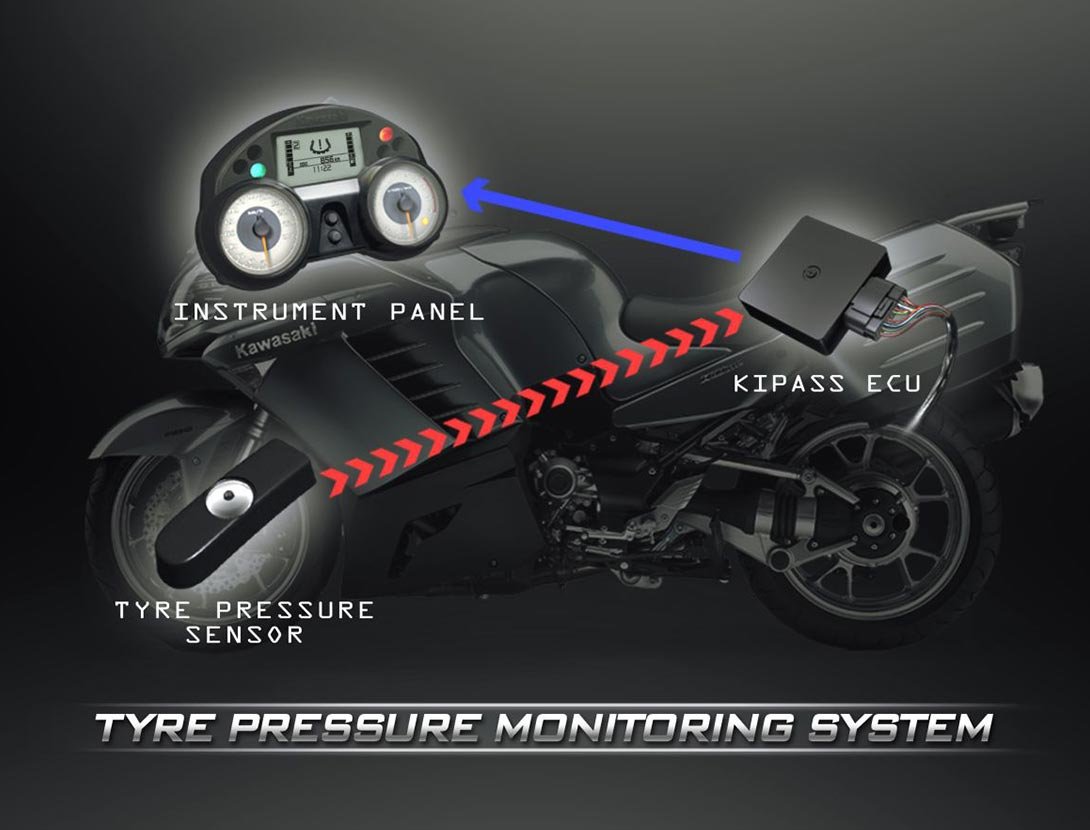 TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING SYSTEM (TPMS) TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING SYSTEM (TPMS)
Maintaining the correct tire air pressure is very important as it can greatly affect a motorcycle's performance. Tire air escapes naturally over time, so it is also important to check tire pressure regularly. The Tire Pressure Monitoring System continuously measures tire pressure (using sensors attached to the air valves of each wheel) and displays the current pressure on the bike's instrument panel while riding.
Tire air pressure varies greatly as the tires warm up, but the Tire Pressure Monitoring System takes this into consideration and recalculates the pressure for 20°C (68°F) to avoid confusion and false warnings. |
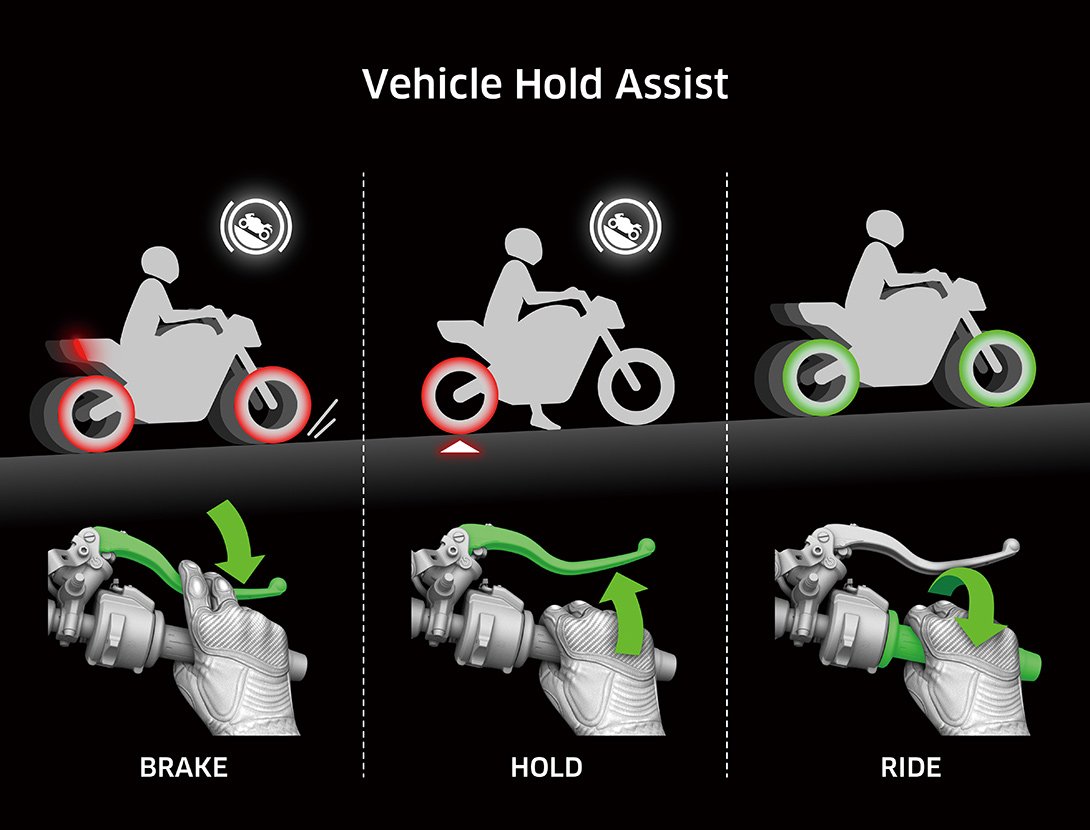 VHA (Vehicle Hold Assist) VHA (Vehicle Hold Assist)
VHA (Vehicle Hold Assist):
Activated when the rider has stopped and firmly applies the brake(s), VHA engages the rear brake to allow the rider to relax their brake hand/foot.
In addition to brake fluid pressure, the system examines the degree of road slope, front/rear wheel speed, throttle position, and side stand switch to determine whether operation conditions have been met. When the rider has stopped, VHA is initiated after the rider exerts a given amount of pressure (to either the front and/or rear brake). The ABS pump exerts pressure to engage the rear brake, and a light/signal is indicated on the instrument panel to let the rider know that they can relax their brake hand (and foot) and the bike will remain in place. |












 Engine Management Technology
Engine Management Technology
 ECONOMICAL RIDING INDICATOR
ECONOMICAL RIDING INDICATOR



 KTRC (KAWASAKI TRACTION CONTROL)
KTRC (KAWASAKI TRACTION CONTROL)





 FCW (Forward Collision Warning)
FCW (Forward Collision Warning) IMU-ENHANCED CHASSIS ORIENTATION AWARENESS
IMU-ENHANCED CHASSIS ORIENTATION AWARENESS Kawasaki SPIN
Kawasaki SPIN KECS (KAWASAKI ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION)
KECS (KAWASAKI ELECTRONIC CONTROL SUSPENSION) KIBS (KAWASAKI INTELLIGENT ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
KIBS (KAWASAKI INTELLIGENT ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) KIPASS (KAWASAKI'S INTELLIGENT PROXIMITY ACTIVATION START SYSTEM)
KIPASS (KAWASAKI'S INTELLIGENT PROXIMITY ACTIVATION START SYSTEM) TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING SYSTEM (TPMS)
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING SYSTEM (TPMS) VHA (Vehicle Hold Assist)
VHA (Vehicle Hold Assist)